How to Beat Level 9 in I'm Not a Robot - Nested Squares Guide
TL;DR
- Objective: Conquer Level 9 of Neal.Fun's 'I'm Not a Robot' by progressively selecting nested squares containing stop signs.
- Steps: Select initial stop sign squares, watch for subdivision, continue selecting at each new level until no further nesting occurs.
- Target: Approximately 31 tiny squares selected across multiple subdivision levels.
- Risk: Missing selections at any level or selecting incorrect squares will prevent successful completion.
This guide provides a comprehensive approach to mastering Level 9 of Neal.Fun's 'I'm Not a Robot' game, specifically the complex nested selection challenge. Players often find this level overwhelming due to its multi-layered progression and the precision required at each subdivision stage. This article breaks down the nested selection process into manageable steps, ensuring systematic completion of this intricate puzzle.
Unlocking Level 9: The Nested Selection Mechanism Explained
Level 9 of Neal.Fun's 'I'm Not a Robot' game introduces a sophisticated multi-layered selection system that challenges players to navigate through progressive subdivisions while maintaining accuracy in stop sign identification. Unlike previous levels that require single-stage selection, this puzzle demands sustained attention across multiple subdivision cycles, with each level revealing increasingly granular detail. The challenge lies not just in identifying stop signs, but in managing the cognitive load of tracking selections across multiple nested layers while maintaining precision at each stage.
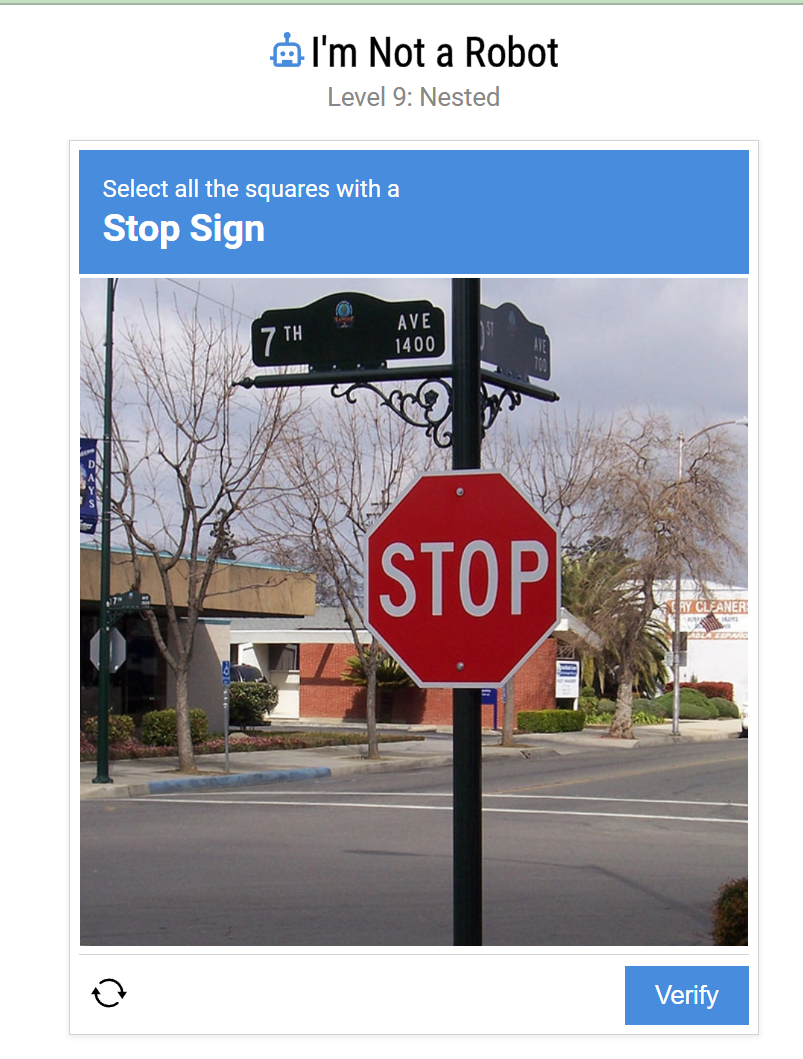
Level 9 Nested Squares Overview
Mastering Nested Selection: A Comprehensive Multi-Stage Strategy Guide
The key to successfully navigating Level 9 of 'I'm Not a Robot' lies in understanding the progressive subdivision mechanism and maintaining systematic selection accuracy across all nested levels. The puzzle begins with a standard grid but evolves through multiple subdivision stages, each requiring careful analysis and precise selection. Follow these detailed steps to complete the nested selection process:
Stage 1: Initial Grid Analysis and Primary Selection
- Objective: Identify and select all visible stop signs in the initial grid configuration.
- Procedure: Scan the entire grid systematically for octagonal red stop signs. Click on each square containing a clearly visible stop sign. Pay attention to partially visible signs at square boundaries, as these often indicate valid selections. Ensure comprehensive coverage of the initial grid - missing selections at this stage will cascade through all subsequent subdivision levels.
Stage 2: First Subdivision Response and Secondary Selection
- Objective: Navigate the first subdivision cycle and identify stop signs in the newly created smaller squares.
- Procedure: After initial selections, observe as selected squares subdivide into four smaller squares each. Examine each new subdivision carefully for stop signs that may not have been visible at the previous resolution level. Select all squares containing stop signs in this new, more detailed view. The subdivision process reveals additional detail that was not apparent in the initial grid.
Stage 3: Progressive Subdivision Management
- Objective: Continue the selection process through multiple subdivision cycles until no further nesting occurs.
- Procedure: Repeat the selection process for each subsequent subdivision level. Each cycle will reveal increasingly fine detail, potentially exposing stop signs that were previously hidden or unclear. Maintain systematic scanning patterns and avoid rushing through subdivisions. The process typically continues for 3-4 subdivision levels, with each level requiring careful analysis and precise selection.

Level 9 Progressive Selection
Stage 4: Final Verification and Completion Assessment
- Objective: Ensure all stop signs have been identified across all subdivision levels and verify the target selection count.
- Procedure: After the subdivision process concludes (when squares no longer subdivide upon selection), verify that approximately 31 squares are selected total. This count represents the cumulative selections across all subdivision levels. If the count is significantly different, review recent selections for potential errors or missed stop signs.
Advanced Subdivision Strategies and Pattern Recognition
- Boundary Analysis: Stop signs often appear at the edges of squares, spanning multiple subdivisions. These boundary cases require careful attention as they may become more clearly defined at higher subdivision levels.
- Progressive Refinement: Each subdivision level provides increased resolution and detail. Signs that appear ambiguous at one level may become clearly identifiable at the next subdivision stage.
- Systematic Scanning: Develop consistent scanning patterns for each subdivision level to avoid missing selections. Consider using grid-based approaches (row-by-row or column-by-column) to ensure comprehensive coverage.
Behind the Challenge: Understanding Recursive Selection Systems
Neal.Fun's Level 9 represents a sophisticated implementation of recursive user interface design, where user actions trigger progressive system responses that require continued user engagement. This puzzle simulates the complexity of hierarchical data structures and progressive disclosure interfaces commonly found in advanced software systems. The nested selection mechanism tests players' ability to maintain context and accuracy across multiple interaction layers while managing increasing cognitive complexity.
The challenge serves as both entertainment and education about the principles of progressive refinement and hierarchical information organization. Real-world applications of similar concepts include image zoom systems, hierarchical file browsers, and multi-level data visualization tools. The puzzle demonstrates how user interfaces can guide users through complex information spaces by revealing detail progressively rather than overwhelming them with complete information simultaneously.
Pro Tips for Conquering Multi-Level Selection Challenges
Mastering Level 9 and similar nested selection puzzles requires developing systematic approaches to hierarchical navigation and maintaining accuracy across multiple interaction stages. These strategies will improve your success rate in complex, multi-stage challenges.
Tip 1: Develop Subdivision Awareness
- Objective: Build expertise in predicting and managing subdivision behavior.
- Details: Understand that each selection triggers a subdivision event that requires immediate attention. Develop the habit of examining subdivided areas immediately after each selection cycle. Don't rush to the next selection until you've thoroughly analyzed the current subdivision results.
Tip 2: Implement Progressive Counting Strategies
- Objective: Track selection progress across multiple subdivision levels to ensure target achievement.
- Details: Maintain awareness of your total selection count as you progress through subdivision levels. The target of approximately 31 selections provides a useful benchmark for completion assessment. If your count deviates significantly from this target, review your selection strategy for potential improvements.
Tip 3: Master Visual Pattern Recognition at Multiple Scales
- Objective: Develop the ability to identify stop signs consistently across different resolution levels.
- Details: Stop signs maintain their octagonal shape and red color across subdivision levels, but their apparent size and clarity change. Practice identifying these consistent visual elements regardless of scale. Focus on shape recognition rather than size-based identification.
Tip 4: Manage Cognitive Load Through Systematic Approaches
- Objective: Prevent mental fatigue and maintain accuracy throughout the multi-stage process.
- Details: Break the challenge into discrete stages rather than attempting to process all information simultaneously. Complete each subdivision level thoroughly before moving to the next. Take brief mental breaks between major subdivision cycles to maintain optimal performance.
Frequently Asked Questions About Nested Selection Challenges
Players often encounter similar difficulties when tackling Level 9's complex multi-stage selection requirements. Here are answers to the most common questions:
-
Q1: How do I know when the subdivision process is complete?
- A1: The subdivision process concludes when selected squares no longer subdivide upon clicking. You'll notice that clicking on squares no longer triggers the creation of smaller squares, indicating that maximum subdivision depth has been reached.
-
Q2: What should I do if I accidentally select a square without a stop sign?
- A2: Click the incorrectly selected square again to deselect it. The system allows you to correct mistakes by toggling selections. However, be aware that deselecting a square that has already subdivided may affect the subdivision state.
-
Q3: Why does my selection count differ significantly from the target of 31?
- A3: Significant deviations from the target count usually indicate either missed stop signs at one or more subdivision levels, or incorrect selections of squares without stop signs. Review your selections systematically, focusing on areas where you may have missed obvious stop signs.
-
Q4: How can I improve my accuracy in identifying stop signs across different subdivision levels?
- A4: Focus on consistent visual elements: octagonal shape and red color. These characteristics remain constant across subdivision levels. Develop systematic scanning patterns and avoid rushing through subdivision analysis.
-
Q5: Is there a specific order I should follow when selecting squares?
- A5: While there's no required selection order, systematic approaches (such as left-to-right, top-to-bottom scanning) can help ensure comprehensive coverage and reduce the likelihood of missing stop signs.
Final Summary
Successfully completing Level 9 of 'I'm Not a Robot' requires mastering progressive subdivision navigation while maintaining consistent stop sign identification accuracy across multiple nested levels. The challenge tests your ability to manage complex, multi-stage interactions while tracking cumulative progress toward the target selection count. Master this level by developing systematic subdivision analysis techniques, implementing progressive counting strategies, and maintaining focus on visual pattern recognition across varying scales. Remember that patience and systematic approaches are more effective than speed, as accuracy at each subdivision level is crucial for overall success.